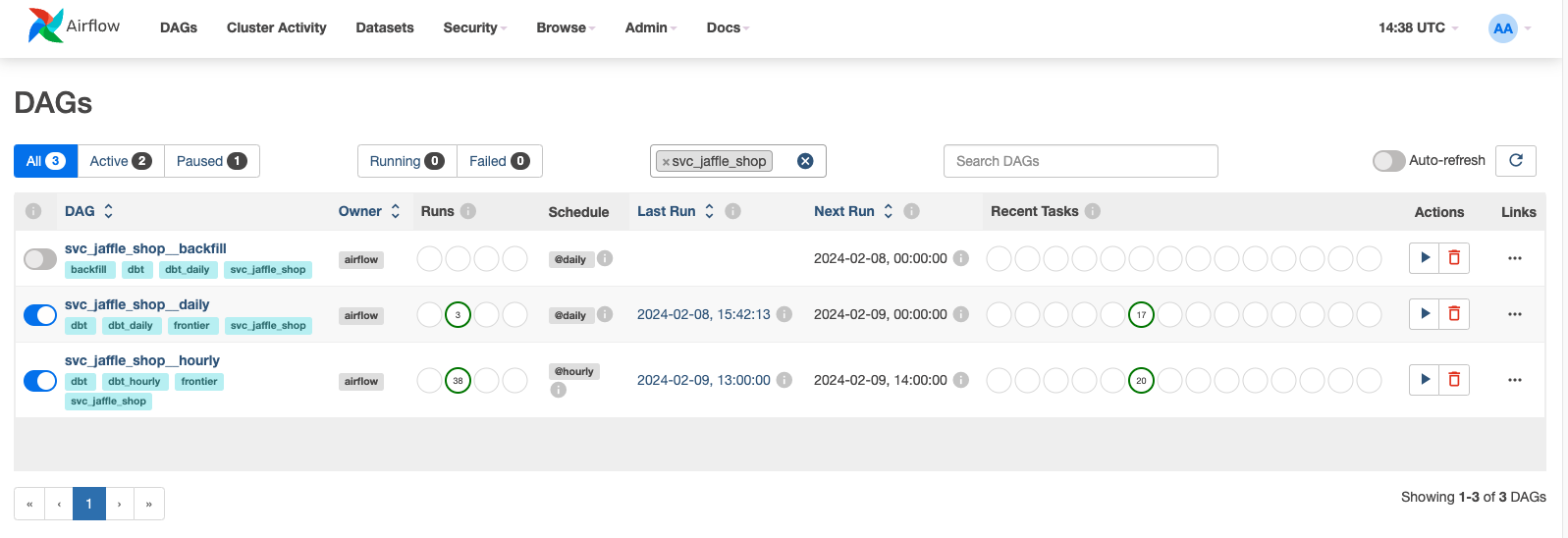
Running the basic project¶
As an example, we use the jaffle_shop dbt project with some useful modifications. As dmp-af is domain-oriented tools, there's domain svc_jaffle_shop in the example. It's a simple domain with all the models, tests and seeds.
DAG files: examples/dags/
Modifications: 1. Models on staging layer have @daily scheduling. They appear in svc_jaffle_shop__daily Airflow DAG that has daily scheduling. 2. Models customers and orders have @hourly scheduling. Models in svc_jaffle_shop domain with @hourly scheduling appear in svc_jaffle_shop__hourly DAG. All cross-domain or cross-scheduling dependencies are resolved by waits (sensors in Airflow). 3. Dbt project structure is modified to have domain-layered structure.
Here's the DAGs layout:
| Hourly DAG | Daily DAG |
|---|---|
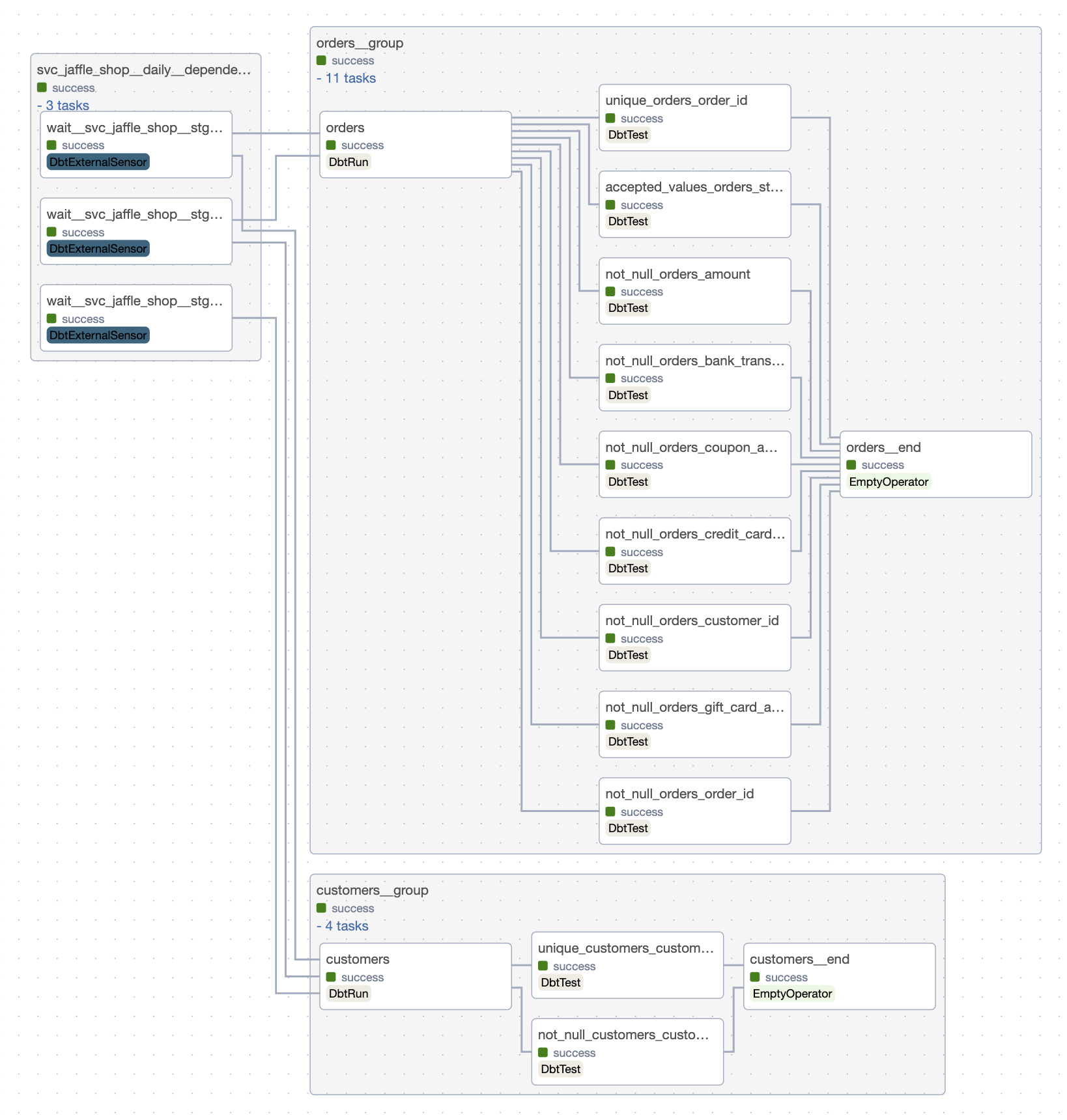 | 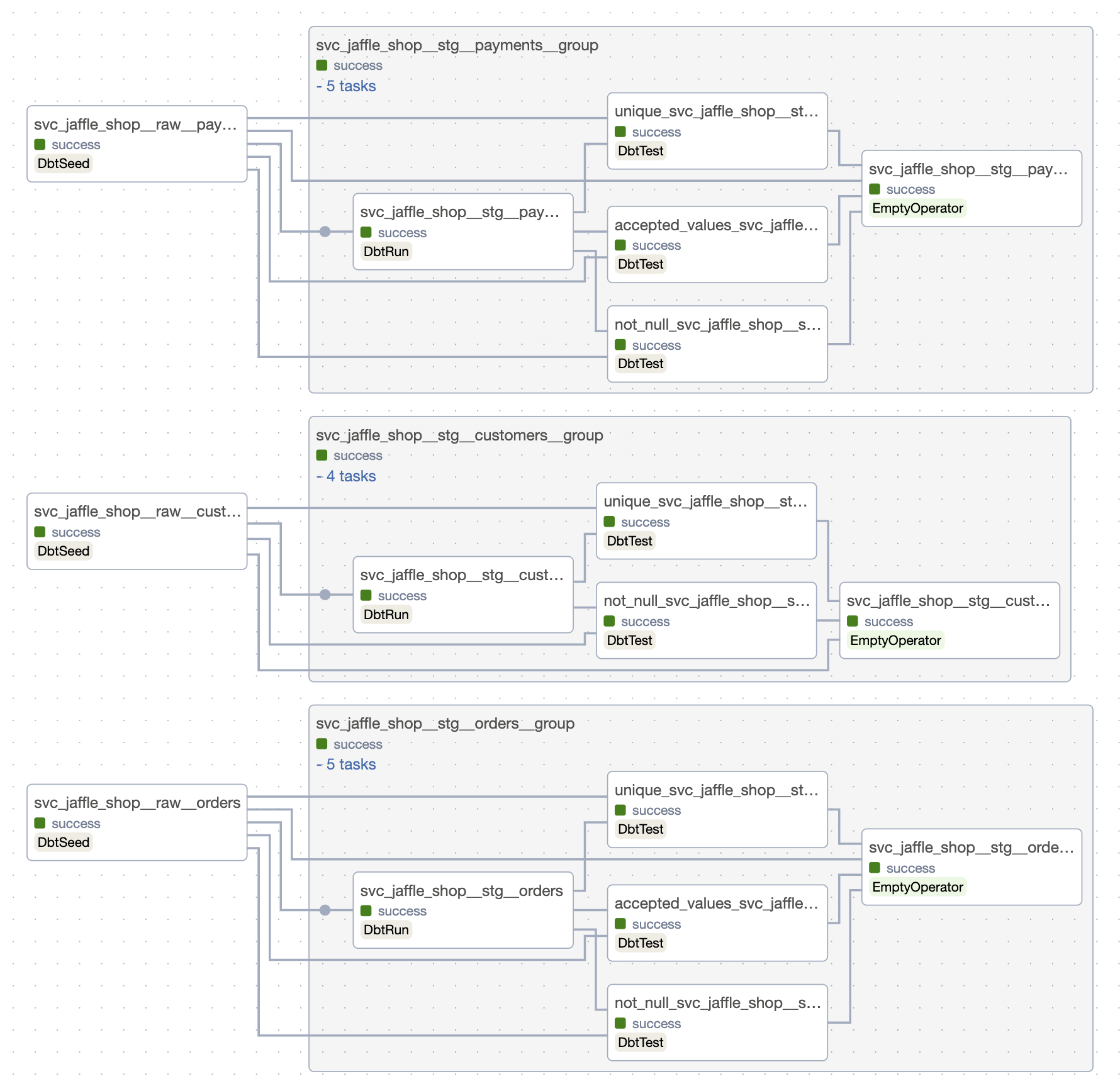 |
Backfill DAGs¶
You may notice that dmp-af generated also backfill DAGs with naming patten <domain_name>__backfill. These DAGs have @daily scheduling, but they are made to be triggered manually.
The main purpose of these DAGs is to backfill the data in case of any issues with the regular DAGs. The backfill DAGs are generated for all domains, and they are not dependent on each other.
To backfill any data interval, you need just to trigger the DAG with the specific date interval, and it will run all the models with tests in one domain.
Single model DAG¶
By default dmp-af will generate unified DAG with name <dbt_project_name>_dbt_run_model. This DAG is made for manual run of a single model. It's useful for debugging or backfilling a single model with specified date interval.
To turn off just set include_single_model_manual_dag to False in the dmp-af configuration.
from dmp_af.conf import Config
config = Config(
# ...
include_single_model_manual_dag=False,
# ...
)
List of Examples¶
- Advanced Project: several domains, medium and large tests, and different targets.
- Dependencies management: how to manage dependencies between models in different domains.
- Manual scheduling: domains with manual scheduling.
- Maintenance and source freshness: how to manage maintenance tasks and source freshness.
- Kubernetes tasks: how to run dbt models in Kubernetes.
- Integration with other tools: how to integrate dmp-af with other tools.
- [Preview] Extras and scripts: available extras and scripts.